Are you struggling to make the most of your warehouse space? This is a common challenge for many businesses as inventory levels fluctuate and customer demands keep changing. Warehouse capacity planning ensures that your storage space is used efficiently to meet business needs without wasting resources.
According to a report, 20% of warehouses say improving space utilization is one of their top priorities. This shows how important it is for businesses to manage storage effectively.
With good planning, companies can avoid overcrowding, reduce operational delays, and control costs. It also helps them stay prepared for unexpected changes in demand. So, let’s find out how you can do it too.
What Is Warehouse Capacity Planning?
Warehouse capacity planning is the process of organizing and optimizing the storage space in a warehouse to ensure it can efficiently handle current and future inventory levels. It involves analyzing the available space, forecasting product demand, and planning for peak seasons or sudden changes in stock requirements.
The goal of capacity planning is to strike the right balance between storage and accessibility. This means making sure there is enough space to store products without overcrowding, while also ensuring that items can be retrieved quickly when needed. By doing this, businesses can avoid bottlenecks, reduce costs, and improve order fulfillment.
Why Is Warehouse Capacity Planning Important?
Warehouse capacity planning helps businesses run smoothly and efficiently. It makes sure storage space is used properly to avoid problems like crowded areas or empty shelves. With efficient planning, you can save money by reducing the need for extra space and preventing too much stock or not enough of it.
Without planning, it’s easy to lose track of products or delay orders. This can upset customers and cause lost sales. Too much empty space also means paying for storage you don’t need.
Additionally, when you know how much space you have left, you can make better make or buy decisions to come up with the right amount of inventory at the best rates.
Planning ahead helps businesses handle busy seasons or sudden increases in demand. It ensures there’s enough space for inventory and that everything is easy to find. This makes work faster and smoother for employees.
How to Optimize Your Warehouse
Optimizing your warehouse means making the best use of space, time, and resources to keep operations smooth and cost-efficient. Let’s look at some effective ways to do it:
Organize Inventory Smartly
Store similar items together and place high-demand or fast-moving products near the packing or shipping areas. This makes it quicker for employees to pick these items and fulfill orders.
Grouping items logically, like by category or season, also reduces the chances of misplaced inventory and speeds up the picking process. You can also use safety stock optimization to have the right balance between inventory and service level.
Use Vertical Space
Many warehouses only focus on floor space, but using vertical space can greatly increase storage capacity. Installing taller racks or shelves allows you to store more products without expanding your warehouse.
You can also add mezzanine floors to create additional working or storage areas. Just make sure that your equipment, like forklifts, can reach those higher shelves safely.
Use Efficient Picking Methods
Picking strategies, like batch picking or zone picking, save time by minimizing unnecessary movement inside the warehouse.
For example, batch picking allows employees to pick multiple orders at once, while zone picking assigns workers to specific sections. These methods reduce travel time and make order fulfillment faster.
Regularly Review and Forecast Inventory Needs
Keeping track of sales trends and future demand helps you adjust inventory levels in advance. Regular reviews prevent overstocking, which takes up space and increases costs, and stockouts, which lead to missed sales.
Forecasting allows you to prepare for peak seasons and adjust storage accordingly, so you always have the right amount of stock on hand.
Keep the Warehouse Clean and Safe
A clean, well-organized warehouse is easier to work in and helps avoid delays. Clear aisles make it safer for employees to move around and prevent accidents.
Regular maintenance of equipment, like forklifts and conveyor belts, reduces the chance of breakdowns. Ensuring safety also boosts employee morale, leading to better performance.
How to Calculate Warehouse Storage Capacity
Here’s a simple way to calculate it:
1. Measure the Total Warehouse Space
Start by finding the total square footage or cubic footage of your warehouse. Multiply the length by the width (for square footage) or by the height (for cubic footage) to know the full area available.
Formula for cubic footage:
Length × Width × Height
2. Identify Usable Space
Not all space in a warehouse is usable for storage. Subtract the space used for walkways, loading areas, office spaces, and equipment. This gives you the usable storage area.
Example: If your warehouse is 10,000 sq ft but 2,000 sq ft is taken up by walkways and offices, the usable space is 8,000 sq ft.
3. Calculate Storage Space Per Rack
Measure the dimensions of the racks or shelves you use. Find out how many of these racks fit into the usable space. Multiply the height, width, and depth of each rack to get the total cubic storage volume per rack.
Example: A rack that is 8 ft tall, 4 ft wide, and 3 ft deep will have:
8 × 4 × 3 = 96 cubic feet per rack.
4. Factor in Storage Efficiency
Warehouses rarely use 100% of their storage capacity because of factors like air circulation, aisle space, and product shapes. Apply a storage efficiency factor, usually around 80-90%, to get a realistic idea of how much space you can actually use.
Formula:
Total usable space × Storage efficiency (%) = Actual storage capacity
Example: If your usable storage is 8,000 cubic feet and the efficiency is 85%, your actual storage capacity is:
8,000 × 0.85 = 6,800 cubic feet.
5. Calculate Product Volume and Capacity Usage
Measure the size of the products you store and divide the actual storage capacity by the product volume. This will tell you how many items or pallets you can fit.
Example: If each pallet takes up 100 cubic feet, the total number of pallets that can fit is:
6,800 ÷ 100 = 68 pallets.
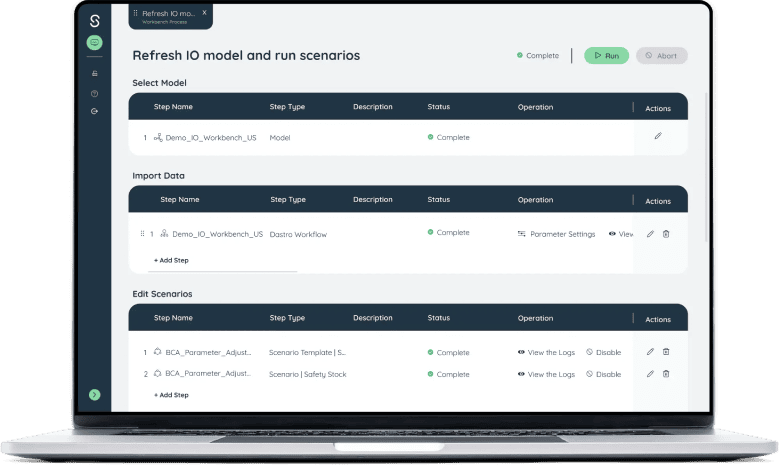
Plan for Long-Term Success with Sophus X
Struggling to balance capacity with fluctuating market demands?
Sophus X offers a Long-Term Capacity Planning solution to help businesses like yours stay ahead. Our platform recommends the best investments, optimizes production sites, and provides strategies to handle seasonal changes.
Whether you need to add shifts, expand capacity, or improve supply chain efficiency, we’ll help you make decisions that improve your return on assets by 20-25% and reduce costs by 10%.
Contact us today to learn how Sophus X can transform your capacity planning and maximize your business potential!